Understanding and Managing Hyperhidrosis Hyperhidrosis is a medical condition characterized by excessive sweating that exceeds the normal requirements for body temperature regulation. For those affected, sweating can occur even without physical exertion or exposure to heat, significantly impacting daily life. This condition can cause discomfort, embarrassment, and sometimes lead to social isolation. In this article, …
Understanding and Managing Hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis is a medical condition characterized by excessive sweating that exceeds the normal requirements for body temperature regulation. For those affected, sweating can occur even without physical exertion or exposure to heat, significantly impacting daily life. This condition can cause discomfort, embarrassment, and sometimes lead to social isolation. In this article, we will delve into the types, causes, and various treatment options for hyperhidrosis, aiming to provide a comprehensive guide to managing this challenging condition.
What is Hyperhidrosis?
Hyperhidrosis involves overactive sweat glands, leading to excessive sweating in specific areas of the body or, in some cases, all over. This condition is more than just a nuisance; it can interfere with daily activities and affect emotional well-being.
Types of Hyperhidrosis
There are two main types of hyperhidrosis: primary (idiopathic) hyperhidrosis and secondary hyperhidrosis.
Primary (Idiopathic) Hyperhidrosis
Primary hyperhidrosis is the most common form and typically begins during adolescence. It primarily affects specific areas such as the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, underarms, and face. The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to be due to overactive sweat glands. This type of hyperhidrosis is not caused by any underlying medical condition and often runs in families, suggesting a genetic component.
Secondary Hyperhidrosis
Secondary hyperhidrosis is less common and usually results from an underlying medical condition or the use of certain medications. Conditions that can cause secondary hyperhidrosis include hormonal imbalances (such as those associated with menopause or thyroid problems), infections, diabetes, and nervous system disorders. Unlike primary hyperhidrosis, secondary hyperhidrosis often results in generalized sweating rather than sweating localized to specific areas.
Causes of Hyperhidrosis
The causes of hyperhidrosis can be multifactorial:
- Genetics: Family history can play a significant role in primary hyperhidrosis.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions like menopause and hyperthyroidism can lead to excessive sweating.
- Medications: Some drugs, including antidepressants and medications for high blood pressure, can cause increased sweating.
- Infections: Tuberculosis and other infections can trigger secondary hyperhidrosis.
- Nervous System Disorders: Disorders affecting the autonomic nervous system can lead to excessive sweating.
Symptoms of Hyperhidrosis
The primary symptom of hyperhidrosis is excessive sweating that is disproportionate to the environment or activity level. Symptoms include:
- Visible sweating that soaks through clothing or drips off the hands.
- Sweating that interferes with daily activities, such as holding a pen, using a computer, or shaking hands.
- Skin infections due to prolonged exposure to moisture.
- Emotional distress or social withdrawal due to embarrassment.
Diagnosis of Hyperhidrosis
Diagnosing hyperhidrosis involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. Tests may include:
- Starch-Iodine Test: This test involves applying iodine to the sweaty area and then sprinkling starch over it. The area will turn dark blue where excessive sweating occurs.
- Paper Test: Special paper is placed on the affected area to absorb sweat, and then it is weighed to determine the amount of sweat produced.
Treatment Options for Hyperhidrosis
Treatment for hyperhidrosis depends on the severity of the condition and the impact on the individual’s life. Here are some common approaches:
Antiperspirants
Over-the-counter or prescription-strength antiperspirants containing aluminum chloride can help reduce sweating. These are applied to the affected areas, usually at night when sweating is minimal, to block the sweat glands.
Medications
Oral medications, such as anticholinergics, can reduce sweating by blocking the nerve signals that trigger sweat glands. However, these medications can have side effects, including dry mouth, blurred vision, and urinary retention, and are generally reserved for more severe cases.
Laser Treatment
Laser treatment involves using a device that delivers heat to the targeted sweat glands, effectively ablating the affected areas. This treatment can provide long-lasting results and is often used for excessive underarm sweating.
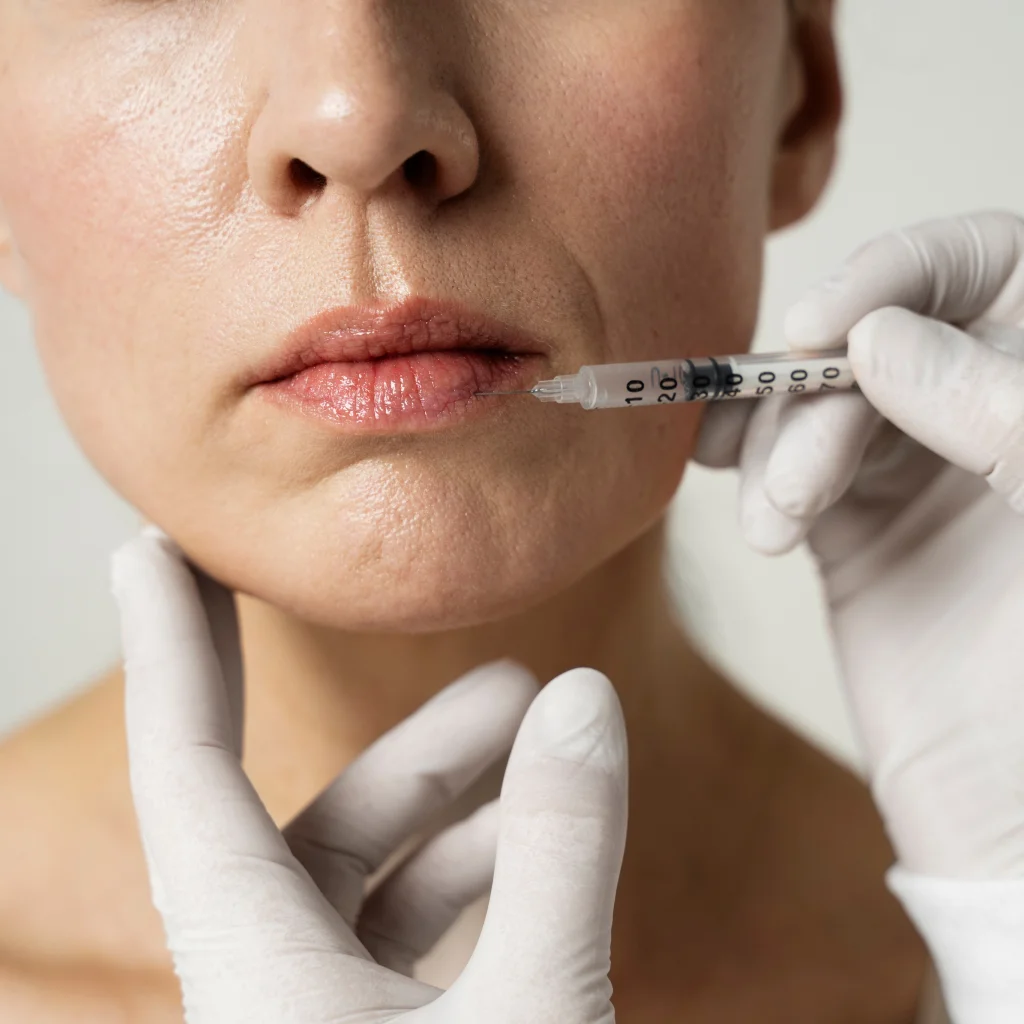
Botox Injections
Botox injections can temporarily block the nerve signals that stimulate sweat production. This treatment is particularly effective for excessive underarm sweating and can last for several months before additional treatments are needed.
Medical Procedures
For severe cases of hyperhidrosis that do not respond to other treatments, surgical options may be considered:
- Sympathectomy: This procedure involves cutting or clamping the nerves that trigger sweating in specific areas. It is usually reserved for severe cases of palm or face sweating.
- MiraDry: A non-invasive treatment that uses electromagnetic energy to destroy sweat glands.
Prescription Medications
Recent advancements have led to the development of prescription medications that specifically target the nerve signals responsible for sweat gland activation. These medications can be particularly effective for treating primary axillary hyperhidrosis (excessive underarm sweating).
Lifestyle Changes
Simple lifestyle modifications can also help manage hyperhidrosis:
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid triggers such as spicy foods, caffeine, and stress.
- Clothing Choices: Wear moisture-wicking clothing that can help keep the skin dry.
- Hygiene: Maintain good hygiene by showering regularly and using antibacterial soap to reduce body odor.
- Stress Management: Practices like yoga, meditation, and relaxation exercises can help manage stress, which can exacerbate sweating.
The Psychological Impact of Hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis can have a significant psychological impact, leading to anxiety, depression, and social isolation. It is essential to address the emotional aspects of this condition. Support groups, therapy, and speaking with a mental health professional can provide coping strategies and emotional support.
Seeking Professional Help
If you suspect you have hyperhidrosis, it is important to seek professional help. A healthcare provider can help determine the cause of excessive sweating and recommend appropriate treatments. They can also monitor your condition and adjust treatments as necessary.
Conclusion
Hyperhidrosis is a challenging condition that can significantly impact quality of life. However, with the right diagnosis and treatment plan, it is possible to manage symptoms effectively. From antiperspirants and medications to advanced treatments like Botox and laser therapy, there are numerous options available to help reduce excessive sweating. Lifestyle changes and professional support can also play a crucial role in managing this condition.